Not knowing what to do,
I telephoned the police. (=Because I didn't know what to do,...) He зная, что делать, я позвонил в полицию. Однако в научно-технической литературе вы можете встретить независимые причастные обороты. В независимом причастном обороте имеется существительное без предлога (реже местоимение в именительном падеже), которое стоит перед причастием и по смыслу является субъектом действия, выраженного причастием. От основной части предложения этот оборот всегда отделяется запятой:
Oil consists of a mixture of hydrocarbons, some other compounds being also present. Нефть состоит из смеси углеводородов, кроме того, в ней присутствуют также некоторые другие соединения. Unit 9
Если независимый причастный оборот стоит в начале предложения, то он переводится на русский язык обстоятельственным придаточным предложением причины, времени или условия. Если независимый причастный оборот стоит в конце предложения, то он переводится на русский язык предложением, вводимым союзами причем, а, и: Good results having been obtained, the researchers could continue the experiment. At this mine the method of working is longwall, the faces being rather long. После того как (Когда) были получены хорошие результаты, исследователи смогли продолжить эксперимент. На этой шахте применяется система разработки длинными столбами, причем забои бывают достаточно длинными. Субъект независимого причастного оборота может также вводиться предлогом with: With Peter working in Так как Питер работал в London, the house Лондоне, дом совсем seemed empty. опустел. ПРЕДТЕКСТОВЫЕ УПРАЖНЕНИЯ 1. Прочитайте вслух следующие слова: [ае] —ex'tract, 'gravel, 'narrow, 'shallow, 'handle, 'latter [a: ] — 'opencast, part, hard, car,, over'cast,, over'casting [i: ] —cheap, heap, need, reach [a] — 'shovel, 'number, pump, dump [ei] —'basic, 'breaking, de'cade, waste, rail [ou] — open, load, un'load, 'process, whole, stone [au] — doubt, mount, power, 'in'side, 'out'side 2. Прочитайте следующие слова и сочетания слов 1-2 раза про себя, break [breik] v (broke [brouk], broken ['broukn]) отбивать (уголь или породу), обрушивать кровлю; разбивать; ломать; л отбойка, обрушение; break out отбивать, производить выемку
Unit 9
(руды.или породы); расширять забой; breakage л разрыхление, дробление drill [dnl] л бур;.перфоратор; бурильный молоток; сверло; v бурить; car ~ буровая тележка; mounted ~ перфоратор на колонке; колонковый бурильный молоток; drilling л бурение dump [dAmp] л отвал (породы); склад угля; опрокид; external ~ внешний отвал; Internal ~ внутренний отвал; v сваливать (в отвал); разгружать; отваливать; опрокидывать (вагонетку); dumper опрокид; самосвал; отвалообра-зователь; dumping л опрокидывание; опорожнение; опрокид; syn tip environment [in'vai9r(s)nmsnt] л окружение; окружающая обстановка/среда explode [iks'ploud] v взрывать, подрывать; explosion [iks'plousn] л взрыв; explosive л взрывчатое вещество; а взрывчатый friable ['frawbl] а рыхлый; хрупкий; рассыпчатый; слабый (о кровле) handle f'haendl] v перегружать; доставлять; транспортировать; управлять машиной; л ручка; рукоять; скоба; handling л подача; погрузка; перекидка, доставка; транспортировка; обращение с машиной heap [hi: p] v наваливать; нагребать; л породный отвал, терри-коник; syn spoil ~, waste ~ hydraulicklng [, hai'dro: likirj] л гидродобыча; гидромеханизированная разработка load [loud] v нагружать, грузить, наваливать; л груз; нагрузка; loader л погрузочная машина, навалочная машина, перегружатель; грузчик; cutter-loader комбайн, комбинированная горная машина lorry ['Ion] л грузовик; платформа; syn truck mention ['men/n] v упоминать overcasting ['ouvaka: stig] л пере-лопачивание (породы) pump [рлтр] л насос; gravel ~ пес-ковый насос; sludge ~ шламовый насос; v качать; накачивать; откачивать reclamation [.rekls'meijn] л восстановление; осушение; извлечение крепи; ~ of land восстановление участка (после открытых работ) sidecastiag [ *saidka: stin] л внешнее отвалообразование site [salt] л участок, место; building ~ строительная площадка slice [slais] л слой; slicing л выемка слоями, разработка слоями strip [strip] v производить вскрышные работы; разрабатывать; очищать (лаву); вынимать породу или руду; л полоса; stripper л забойщик; вскрышной экскаватор; stripping л открытая разработка, открытые горные работы; вскрыша; вскрытие наносов unit ['ju: nit] л агрегат; установка; устройство; прибор; узел; секция; деталь; машина; механизм; единица измерения; участок wasbery ['wo/an] л углемойка; ру-домойка; моечный цех to attract smb's attention привлекать чье-л. внимание not to mention... не говоря уже о...
3. Переведите на русский язык слова с префиксом < /«-, имеющем цательное значение: deformation, demagnetization, demobilization, dewatering Unit 9
4. Определите по суффиксу, какой частью речи являются следующие слом. Переведете их: dig — digger — digging load — unload — loader — loading — unloading strip — stripper — stripping explode — explosion — explosive wash — washing — washery depend — dependent — dependence — independence consume — consuming explore — exploration — exploring — exploratory friable — friability remove — removal — removable — removing dump — dumper — dumping produce — production — productive — product — productivity — producer 5. Прочитайте следующие сочетания слов и переведите их: strip mines independent mechanical units access to the deposit handling equipment mine cars friable ground overburden removal an extracted area low-grade deposits land reclamation waste heaps exploratory workings earth-moving equipment car drills gravel and sludge pumps removal of waste rock ore concentration plants trends towards open-cast operations searching for minerals 6. Определите значения следующих слов по сходству их корней с корнями horizontal slices; type of overburden; the whole production process; the following basic parts; mineral excavation; various mechanical handling equipment; specially equipped permanent stations; in harmony with environment 7. Прочитайте текст А. Назовите основные этапы и перечислите ТЕКСТА Open-cast Mining Minerals at shallow depths are extracted by open-cast mining which is cheaper than underground mining. Open-cast mining consists in removing the overburden, and other strata that lie above mineral or fuel deposits to recover them. Opencasts or open-pit mines are in fact quarries for getting coal or metalliferous minerals. In the USA opencasts are called strip mines (strip pits). All the surface excavations, waste heaps and equipment needed for extracting mineral in the open form an independent mining Unit 9
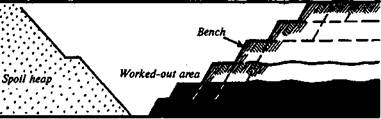
Fig. 9. Open-cast working In opencasts the excavation is by horizontal slices corresponding to the type of mineral or overburden in slice. In Fig. 9 one can see the benches (or slices). A bench is a thickness of rock or mineral which is separately broken or excavated. Other open workings are called trenches, which are long, narrow, shallow exploratory workings. The whole production process in opencasts can be divided into the following basic stages: 1) preparing the site to be worked; 2) de-watering it and preventing inflows of water to the site; 3) providing access (entry) to the deposit by the necessary permanent investment; 4) removal of overburden (stripping); 5) mineral excavation. Stripping the overburden and mineral production include breaking rock or mineral, transporting it and loading it. Minerals can often be dug directly by earth-moving equipment, while to break hard rocks it is necessary to use explosives. Modern methods of working opencasts involve the use of mechanical plants or hydraulicking. The basic units of a mechanical plant are excavators, car drills or other mounted drills, and various mechanical handling equipment whereas the basic units of hydraulicking are monitors, pumps such as sludge pumps or gravel pumps. Hydraulicking can be used in soft or friable ground. Transport operations involve the removal of waste rock or mineral, the latter being transported to coal washeries, ore concentration plants, to power stations, or to a railway station. Waste rock is removed to a spoil heap or dump (tip) either outside the deposit or in an extracted area, these being called external or internal dumps, respectively. 220______________________________________________ Unit The transport used in opencasts are rail cars, large lorries, and conveyers. Sometimes the overburden is stripped and dumped by excavators without other transport, in overcasting or sidecasting. Mineral is usually unloaded at specially equipped permanent stations. Waste rock is dumped at various points which are moved as the work develops. Summing up, mention should be made of the fact that last decades have seen a marked trend towards open-cast operations. Large near-surface (though usually low-grade) deposits offer the possibility of achieving greater outputs. There can be little doubt that the cost per ton of ore mined by underground methods is generally higher than that for open-cast mining. At the same time it is necessary to say that although efforts are made to develop mine sites in harmony with the environment, extraction methods produce some disturbances on the Earth's surface which reduce its economic value. In recent years Russia and other countries have developed national programmes for environmental protection. The aim of such programmes applicable to the mining industry is to control and protect natural resources and regulate reclamation and landscape restoration. УПРАЖНЕНИЯ 8. Укажите, какие предложения соответствуют содержанию текста. Под 1. An opencast is a long, shallow, narrow exploratory working. 2. Explosives are used for excavating hard rocks.
3. Monitors, different types of pumps and other handling 4. Waste rock is always removed to a spoil heap outside the 5. Large near-surface, usually low-grade deposits are extracted 6. Open-cast mining has all the advantages of low-cost production. 9. Ответьте на следующие вопросы: 1. What deposits can be extracted by the open-cast method? 2. What is called an opencast? 3. What is the difference between a trench and an opencast? 4. Is the removal of overburden the first operation in open-cast Unit 9 5. In what case is it necessary to use explosives to break 6. Is hydraulicking used only in open-cast mining? 8. What transport systems are used in opencasts? 9. Where is waste rock dumped? 10. What is the main advantage of open-cast mining? 10. а) Найдите в правой колонке русские эквиваленты следующих слов и сочетаний слов: 1. to consume energy 2. friable roof 3. waste heap (spoil heap) 4. sludge and gravel pumps 5. automatic dumper 6. mounted drill 7. explosives 9. slicing method 10. not to mention... а) автоматический опрокид б) не говоря о (чём-л.) в) перфоратор на колонке г) слоевая система разработки д) слабая кровля е) потреблять энергию ж) отвал, террикон з) песковый и шламовый насосы к) перелопачивание б) Найдите в правой колонке английские эквиваленты следующих слов и сочетаний слов: 1. участок (место) 2. внешнее отвалообразование 3. открытая разработка, вскрыша 4. агрегат (установка) 5. углемойка 6. вскрыша; покрывающие породы 7. гидродобыча 8. грузовик 9. привлекать чье-л. внимание а) washery б) overburden в) site г) sidecasting д) lorry (truck) с) to attract smb's attention ж) landscape restoration з) unit и) stripping к) hydraulicking 11. Подберите к глаголам нз списка А соответствующие существительные из списка Б: А. 1. to attract 2. to dump 3. to extract 4. to offer 5. to prepare 6. to prevent 7. to provide 8. to remove 9. to strip Б. а) the possibility of (doing smth) б) overburden в) waste rock at special points д) the attention е) inflows of water ж) mineral з) access (entry) to the deposit к) explosives 222____________________________________________________ Unit 9 12. Подберите соответствующие определения к следующим словам: 1. The extraction of coal or ore from the seam or vein without 2. A long, wide, comparatively shallow working. 3. A thickness of rock which is separately broken and excavated. 4. A long, narrow, comparatively shallow exploratory working. 5. The extraction of minerals from the exposed area after the 13. •) Переведите предложения, обращая внимание на перевод незави 1. Mineral reserves suitable (пригодный) for open-cast mining 2. The discovery of such deposits as coal, shale, iron, 3. The most widely used hydraulic method of mining involves 4. The type of power which drives mining machines can be 5. Russian coals are of high quality, only 20 per cent being 6. Different kinds of exploratory drilling are used, their choice 7.The mine being gassy, flameproof equipment had to be used. 8. Reliable communication being essential on the surface and underground, automatic and remote control systems are widely used. б) Найдите в тексте А предложения, в которых употребляется независимый причастный оборот, и переведите их на русский язык. 14. Переведите предложения, обращая внимание на способы выражения 1.Large shovels are to be used in strip mines because they can handle all types of mineral, including blocky material. Unit 9_____________________________________________ 223 2. Draglines are normally used for handling unconsolidated and 3. Scrapers have good mobility. Their use should be limited to 4. Bucket-wheel excavators must be widely used in open-cast 5. Many factors have to be taken into consideration in 15. а) Найдите в тексте А и переведите предложения, в которых глагол- б) Найдите в тексте А н переведите предложения, в которых употребляется: 1) герундий; 2) причастные обороты; 3) инфинитив в функции определения; 4) сложноподчиненные предложения. 16. Переведите предложения, используя следующие слова н сочетания
|