Section VIII. Biologically important heterocyclic compounds.
1. What the name of compounds which have the following structure?
2. What is title corresponds to the following compound?
3. Which derivatives of nucleotide bases are adenine and guanine? 4. What are condensed nuclei formed purine? 5. Which vitamins belong to nicotinamide? 6. What the name of compounds formed from uracil and β-D-ribofuranose? 7. What is the bond formed by the phosphorylation of GDF (guanozin-5/-diphosphat)? 8. Which type of bond forms during the interaction of uridine with phosphoric acid? 9. Which type od bond forms during the interaction uracil with D - ribose? 10. What product is formed in the hydrogenation of pyridine? 11. What mechanism of nitration of pyridine? 12. What is the product formed by the reaction: β-methylpyridine + [O] → 13. What products are formed by complete hydrolysis of thymidylic acid in acidic medium?
14. What is the product formed by the reaction: Pyridine + sulfuric acid →? 15. Which mechanism reaction occurs sulfonation of pyridine and in which position shall sulfo group? 16. What products are formed by the following reaction Uridine + H +, HOH 17. Which product is formed by the following reactio Pyridine + HCl →? 18. Imidazole in the form derivatives of widely distributed in the animal and plant world (vitamin B12). Why even strong oxidants (nitric and chromic acid, alkaline solution of potassium permanganate) hardly oxidized imidazole ring? 19. Inflammatory processes in gout in the joints caused by deposition of monosodium salt of uric acid. Which tautomeric form uric acid participates in the formation of the sodium salt? 20. After heating the compound in the presence of a mineral acid were obtained phosphoric acid, deoxyribose, and guanine, in the ratio of 1:1:1. What the name of this compound?
|

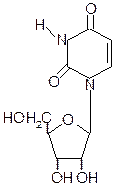

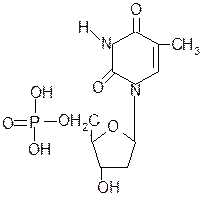
 ?
?


