Test questions
1. What is elastic buckling? 2. What compressive force value do we call critical? 3. What formula can be used to determine the value of the critical force? 4. Point out the domain of the Euler formula application. 5. How does the bar end character influence on the critical force value? 6. Point out the formula to calculate the slenderness ratio of a bar. 7. What do we call the limiting slenderness ratio of a bar? 8. What material characteristics do you have to know to calculate the liming slenderness ratio of a bar? 9. What practical value does the critical bar determination of compressive bars have? 10.Does the critical force value depend on the material elastic property? 11.How many times does the critical force change if you replace the pin-ended bar by a bar damped at each end while testing? 12.The essence of the least squares method. LITERATURE
1.Wiliam A.Nash. Theory and problems of strength of materials. Third edition. - New York: Schaum s outline series, 1994, - 424 p. 2.Feodosiev V.l. Strength of materials. - M.: Science, 1986. - 512 p.
Laboratory work № 3 «Fatigue test under pure bending»
Introduction While in operation a lot of machine parts and construction elements are subjected to loads action, changeable in time. If the stresses level is over a certain one, the material stores rupture, that lead to cracks appearance and final breakage. This disruption happens at stresses much lower than at static action. The process of storing ruptures in the material, under fluctuating stresses that lead to cracks appearance and final breakage is called the fatigue of a material. The material property to resist to this fatigue is called the fatigue resistance. Low-cycle and multiple-cycle fatigue are distinguished. The multiple-cycle fatigue is the fatigue of a material, when macrocracks or full breakage happen at 5·104 cycles and more. The low-cycle fatigue is the fatigue of a material, when macrocracks or full breakage happen in the elastoplastic area before 5·104 cycles. The division into low-cycle and multiple-cycle fatigue is conditional. To calculate the fatigue limit it is necessary to have a number of ultimate limit states properties. One of them is the fatigue limit or the endurance range. The endurance range is the maximum stress at which the specimen doesn’t break before the test base. For steel specimen in usual conditions the test base is 107 cycles, for non-iron metals and high-resistance steels the test base is 108 cycles. The endurance range is determined by experiment. The sequence of specimen loading is set so as to produce the stress state analogous to the working conditions of a part. The main types of loading are: a) pure bending at rotation; b) the same in one plane; c) cross-buckle at console round specimen rotation; d) the same in one plane of round and not round specimen; e) cross-buckle of console round and not round specimen. Tests are also performed at combination of loading types.
Theory
The plastic deformation localization near the rupture crack is the distinctive feature of the fatigue fracture even in cases when a detail or a specimen has been manufactured from a material that the large plastic deformation precedes the analogous static load condition of the rupture. For example, the rupture of the tension cylindrical specimen made of a soft steel, advances the plastic deformation in all the work part, approaching 20-30%. While under the longitudinal sign variable loading of a similar specimen, the fatigue fracture occurs without the essential plastic deformation. And it can be determined by the surface crack character and the material structure, that the plastic deformation has taken place in some small regions. The external breaking consists of two ranges: the range of the gradual crack development and the final rupture range. The gradual crack development has a dull smooth surface, because under the frequent repeating loading the crack ends approach and fall apart, so the crack becomes smooth. The final rupture range has a crystal form due to the cleavage-type rupture. The materials fatigue strength depends on not only the state stress form but the stress change character in time. The stress cycle is called their one-time change corresponding to the full period T changes. The stress change character can be different in time. The simplest sine changes are shown in Fig.1.
Fig. 1. The stresses change during time a) - the symmetrical cycle, b) - the constant sign, c) - the pulse cycle, d) - the variable sign
Let us consider the basic cycle characteristics. The minimum cycle stress relation
For the symmetrical cycle (fig. 1a) we have
where The process of the crack formation under variable stresses is connected with the plastic deformation accumulation. It follows, that the fatigue rupture is determinated only by the stresses The tests for the symmetrical cycle are the most widespread. In this case the received fatigue strength value is noted by The first machine for the fatigue tests was built by A. Wohler in the middle of the XlX-th century. To get the fatigue resistance characteristics we need to conduct more than ten tests of the similar specimens. Each specimen is tested up to the rupture (or up to the cycle base number) only for one stress amplitude. The test process is rather long. Approximately about half the specimens are tested under the stresses having 0,7 - 0,5 level of the ultimate strength The tests are conducted in the following sequence. The 0,7 Wohlers curve is drawn for each specimen using the test data (
The fatigue curve appears as in Fig.2. for low-carbon steel.
Fig. 2. The fatigue curve
Wohlers curve approaches asymptotically to the maximum stress value of the cycle under which the specimen does not break up to the test base. This stress is the
|




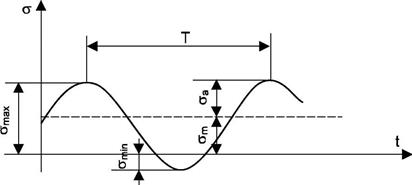
 to the maximum one is called the coefficient of the cycle asymmetry:
to the maximum one is called the coefficient of the cycle asymmetry:
 , and the coefficient of cycle asymmetry r = -1. Two parameters characterize any stress cycle:
, and the coefficient of cycle asymmetry r = -1. Two parameters characterize any stress cycle: ,
, 
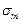 is the average constant cycle stress,
is the average constant cycle stress,  is the cycle amplitude. The difference
is the cycle amplitude. The difference 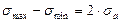 is called the stress scope.
is called the stress scope.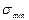 . Besides, as it is shown by experiments, the stress change frequency influence is immaterial. The high temperature tests are the exceptions as well as those under the corrosion medium action. As a result we have to know only the values
. Besides, as it is shown by experiments, the stress change frequency influence is immaterial. The high temperature tests are the exceptions as well as those under the corrosion medium action. As a result we have to know only the values  .
. .
. is put on the ordinate axis and log N is put on the abscess axis.
is put on the ordinate axis and log N is put on the abscess axis.



