Output and price determination
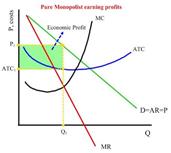
Cost data: Assumption - a pure monopolist hires resources competitively and has the same technology as a purely competitive firm. MR=MC rule: A monopolist seeking to maximize total profit will employ the same rationale as a profit-seeking firm in a competitive industry; they will produce at the point where MR = MC. Profit maximizing price: Find MC= MR and draw a vertical line up to the demand curve. Draw a horizontal line. This is the price they set.
Possibility of losses by monopolist: Pure monopolist’s likelihood of earning economic profit greater than that of purely competitive firm’s. PC – long-run – destined to earn only normal profit. PM has high barriers of entry; therefore, the concept of “entry eliminates profits” does no apply to PM. Pure monopoly does not guarantee profit: Monopoly is not immune from upward-shifting cost curves caused by escalating resource prices. Monopoly is not immune from changes in tastes that reduce the demand for its product. Both of these factors can lead to losses - initially it will persist in operating at a loss and to stop incurring loss, the firm's owners will reallocate their resources.
|