If a general equation of straight line is given, then the distance is determined by the formula
Example. Find the distance from the point М(1;–2) to the straight line 6х–8у+9=0.
LECTURE 5. Analytic geometry in space. Vectors. Simple operations with vectors. The scalar, vector and mixed product of vectors LECTURE PLAN
1. Planes 2. Vectors. Operations with vectors. Planes The general equation of a plane. Suppose given a vector It is required to write an equation of the plane.
M(x,y,z) M0(x0,y0,z0)
According to the general scheme, we take an arbitrary point M(x,y,z) in the plane. Consider the vector Since
Denoting this numerical expression by D, we obtain
This is the general equation of a plane; the coefficients of A,B and C of x, y, and z are the coordinates of the normal vector
The three-intercept equation of a plane. Suppose given a plane not passing through the origin but intersecting the coordinate axes at points
The coefficients are not known yet, so we choose them so, that the plane cuts out the given segments a,b, and c on the coordinate axes. Since, the point
M2 y M1 х Therefore, By analogy, we obtain
Substituting the obtained values of the coefficients А,B, and C into the general equation of the plane, we obtain
which gives, after the reduction by D, the three-intercept equation of the plane:
The equation of a plane passing through three points. Suppose given, three points Following the general scheme, of we take an arbitrary point M(x;y;z) in the plane.
M1 M(x;y;z)
M3
y 0 x The characteristic feature of a plane is that if a point М belongs to the plane, then the three vectors
are coplanar. Therefore, the triple product of these vectors must be zero:
Expressing the triple product in terns of coordinates, we obtain an equation of the plane, passing through the three given points:
Example. Write an equation of the plane passing through the
By formula (24), we have
|

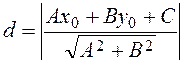 . (16¢)
. (16¢) ,
,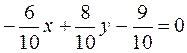 ;
; 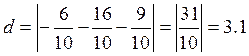 .
. perpendicular to a plane and a point
perpendicular to a plane and a point 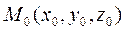 in this plane. This vector is called a normal vector.
in this plane. This vector is called a normal vector.
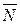
 . For any point in the plane, the vector
. For any point in the plane, the vector  is perpendicular to the normal vector
is perpendicular to the normal vector  .
.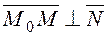 , it follows that the scalar product vanishes:
, it follows that the scalar product vanishes: 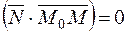 , or, in coordinate form,
, or, in coordinate form, , (*)
, (*)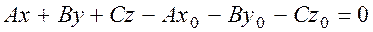 .
.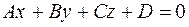 . (23)
. (23) .
. ,
,  , and
, and 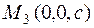 . Suppose also that the segments a,b, and c are known and it is required to write the equation of the plane from the intercepts. Let us write the general equation
. Suppose also that the segments a,b, and c are known and it is required to write the equation of the plane from the intercepts. Let us write the general equation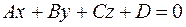 .
. belongs to the plane, its coordinates satisfy the general equation of the plane, and
belongs to the plane, its coordinates satisfy the general equation of the plane, and z M3
z M3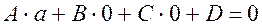 .
. ;
;  .
. ;
;  ;
; 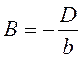 ,
, ;
; 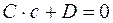 ;
;  .
. ,
, .
.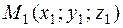 ,
,  , and
, and  . As is known form elementary geometry, there exists a unique plane passing through these points. It is required to write its equation.
. As is known form elementary geometry, there exists a unique plane passing through these points. It is required to write its equation. z M2
z M2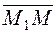 ={x–x1;y–y1; z–z1},
={x–x1;y–y1; z–z1},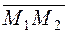 = {x2–x1;y2–y1;z2–z1},
= {x2–x1;y2–y1;z2–z1}, ={x3–x1;y3–y1;z3–z1},
={x3–x1;y3–y1;z3–z1}, .
.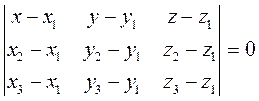 . (24)
. (24) ;
; 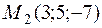 ;
;  .
.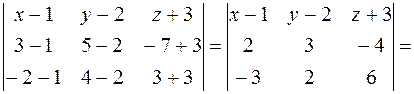
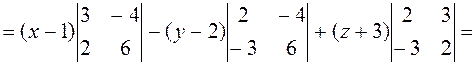
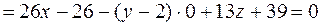 or
or 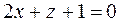 .
.


