The Angle between Planes
Consider the planes given by the equations
which have normal vectors
The condition for two planes to be parallel coincides with the condition for the normal vectors
The perpendicularity conditioin coincides with the perpendicularity condition for the vectors ( Example 1. Show that the following planes are parallel or perpendicular:
The planes are perpendicular, because
Example 2. Write an equation of the plane passing through the point М 0(–1;2; 4) and parallel to the plane 6 x- 7 y+ 5 z+ 11 = 0. The normal vector A(x–x0)+B(y–y0)+C(z–z0)= 0, 6 (x+ 1 )– 7 (y– 2 )+ 5 (z– 4 )= 0; 6 x– 7 y+ 5 z= 0.
z P
0 y x
Take an arbitrary point M(x; y; z) in the planeand consider the radius-vector
For any point М in the plane, the projection of the vector
Consider the scalar product
or, in coordinate form, Thus, we have obtained the normal equation of the plane:
The normalizing factor. Consider the plane given by the general equation Ax+By+Cz+D= 0. It is required to reduce this equation to the normal form (25). Definition. Number m is called the normalizing factor if the equation multiplied by it is normal. To find the normalizing factor, we multiply the general equation of the plane by a number m term by term: mAx+mBy+mCz+mD= 0. This equation is normal if the two normality conditions hold, i.e., 1. (mA)2+(mB)2+(mC)2= 1, 2. mD< 0. From the first condition, taking out m2 and extracting the square root, we find the normalizing factor.
The sign opposite to that of the free term D must be taken.
|

 ;
; 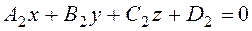 ,
,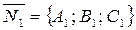 and
and  . Using inner product, we find the cosine of the angle:
. Using inner product, we find the cosine of the angle: .
.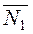 and
and 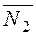 to be collinear:
to be collinear: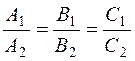 .
.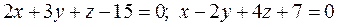 .
. .
.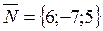 is normal to the required plane also. We have
is normal to the required plane also. We have The normal equation of a plane. Consider a plane. Let us draw the perpendicular ОР from the origin to this plane. Let a,b, and g be the angels between this perpendicular and the coordinate axes x,y, and z, and let
The normal equation of a plane. Consider a plane. Let us draw the perpendicular ОР from the origin to this plane. Let a,b, and g be the angels between this perpendicular and the coordinate axes x,y, and z, and let  . It is required to write an equation of this plane.
. It is required to write an equation of this plane. M(x,y,z)
M(x,y,z) . The unit vector
. The unit vector 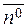 on the perpendicular ОР has the coordinates
on the perpendicular ОР has the coordinates = { cos α; cos b; cos g}.
= { cos α; cos b; cos g}. on the unit vector
on the unit vector  .
. ,
,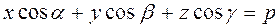 .
.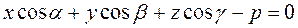 . (25)
. (25)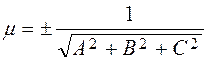 .
.


