The Intersection of a Plane and a straight Line
Suppose given a plane Ax+By+Сz+D= 0
If the straight line and the plane do not intersect, then the parameter t 1does not exist. Suppose, that the line is parallel to the plane; then the vectors
Thus, the parallelism condition for a straight line and a plane is Am+Bn+Cp= 0. Suppose that the line is perpendicular to the plane; then the vectors
This is the perpendicularity condition for a straight line and a plane. Example. Write the equation of a straight line perpendicular to the plane 2 x -3 y +4 z +11=0 and passing through the intersection point of this plane with the line
Let us reduce the canonical equation to the parametric form:
Substituting these expressions for the variables x,y, and z into the equation of the plane 6 t+ 2 – 6 t+ 6 + 4 t+ 1 1= 0. Thus, 4t=–19,
The normal vector to the plane is
The angle between a plane and a straight line. Suppose that a plane in space is determined by its general equation Ax+By+Сz+D= 0, and a straight line is determined by its canonical equations
Using the scalar product of vectors
By the reduction formula,
Definition. A directed interval (or an ordered pair of points) is called a vector.
А
Definition. A vector with coinciding endpoints is called the null vector. Definition. The distance between the head and tail of a vector is called the length Definition. Vectors are collinear if they lie on the same straight line or on parallel lines.
A B C
А 1 В 1
Definition. Vectors are coplanar if they lie in the same plane or in parallel planes. Definition. Two vectors are said to be equal if they are collinear and have the same direction and length.
|

 and a straight line
and a straight line  in space.
in space.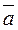 and
and 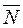 are perpendicular, i.e., or (
are perpendicular, i.e., or ( ·
·  )=0, and Am+Bn+Cp= 0. This means that the denominator vanishes.
)=0, and Am+Bn+Cp= 0. This means that the denominator vanishes.

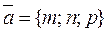
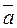 and
and 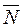 are collinear, i.e., their coordinates are proportional:
are collinear, i.e., their coordinates are proportional: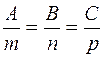 .
. .
.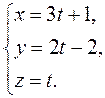
 , and the intersection point of the line with the plane has the coordinates
, and the intersection point of the line with the plane has the coordinates .
. ; since the straight line is perpendicular to the plane, it follows that its direction vector is collinear to the normal vector, i.e.,
; since the straight line is perpendicular to the plane, it follows that its direction vector is collinear to the normal vector, i.e.,  . Thus, the required straight line is determined by the equations
. Thus, the required straight line is determined by the equations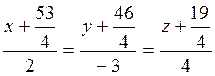 .
.
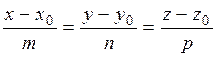 .
.




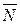
 between the straight line and the plane.
between the straight line and the plane.

 and the general scheme, we determine the angle
and the general scheme, we determine the angle  from the angle between the direction vector
from the angle between the direction vector 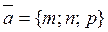 and the normal vector
and the normal vector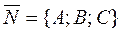 ;
; 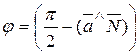 .
.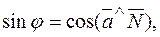 whence
whence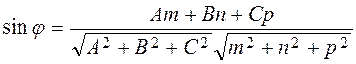 .
. В
В
 , or absolute value of this vector. It is denoted by
, or absolute value of this vector. It is denoted by  .
.

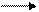

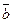

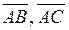 are collinear vectors,
are collinear vectors,
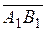 ,
,  are collinear vectors.
are collinear vectors.


